Interior of the Property
Key Elements
General plan
The traffic pattern and layout of rooms is important. Observe the general condition with respect to maintenance and repair.
Living/dining/family room areas
Size and design should be large enough for particular requirements and conveniently located. Any fireplace should have a damper that works and a clean chimney.
Bedrooms
Number should be adequate for present and future uses, with each having an outside window, proper closet space, and entry off a hallway.
Bathrooms
An adequate number of bathrooms is very important and every floor should have a bathroom facility. Check for cracks in tiles, signs of leaks, how long it takes to get hot water, and proper ventilation.
Kitchen
Check appliances such as stove, refrigerator, disposal, dishwasher, and microwave for age, and inquire about present age, condition, and any warranties in effect. Check amount of shelf and counter space, electrical outlets, and storage areas. If a separate breakfast room is not available, there should be adequate space for a kitchen eating area.
Walls and ceilings
Look for major cracks, loose or falling plaster, and any signs of leaks or stains.
Windows and doors
Check to see that windows and doors have adequate locks and open and close properly.
Floors
Walk and jump lightly on floors to determine any movement; check for levelness or bowing.
Stairs
Check for any loose treads or handrails.
Basement
If applicable, basement area should be checked for signs of water leaking, dampness, flooding, dry rot, termites, and for adequate lighting.
Attic
If applicable, the attic should be checked for signs of leaks and any rodent or insect infestation, and if insulated, check type and quantity.
Plumbing system
Check type of water pipes and sewer lines, that can be seen, look for rusting or leaking; turn on faucets to test water pressure; look for clogged or sluggish drains or dripping faucets.
Electrical system
Check load center and observe if there are fuses or circuit breakers; check age and look for signs of wear or exposed wires.
Heating system
Check the type of heating system such as warm air, hot water, or electrical, and determine age and condition. Check for gas leaks and cracked heat exchanger.
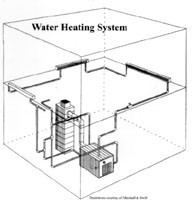
Water heater
Check for signs of leaking or rusting. Determine capacity and recovery rate, age, and condition.
Air conditioning or cooling system
If applicable, check type of air conditioning or cooling system, age, condition, freon, and leaks.
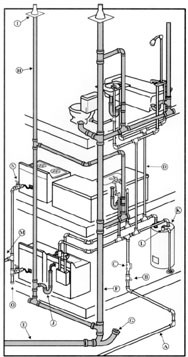
Plumbing System
Main Water Line The main water supply pipe brings water from the street to the home. Older pipe materials may be 1/2" or 3/4" galvanized steel. This type of pipe corrodes internally and may not deliver the volume of water now needed throughout the house. 3/4" copper or plastic pipe is the minimum currently used in modern construction. Normal water pressure is between 35 and 80 PSL. Excessive pressure can wear on valves, fittings, fixtures and appliances.
Water Supply Lines Copper, galvanized, plastic and lead piping have all been used at some time for water systems of residences. Old galvanized piping typically requires replacement due to internal restriction. Lead pipes present a possible health hazard if the lead leaks into the drinking water. A form o plastic piping called "polybutylene" has shown defects from the manufacturing and installation process that can cause leaks. Your inspector is only able to tell you of the condition of the visible piping. No water quality tests are performed during this inspection.
Waste Lines These pipes carry the waste from the house to the sewer system. It is impossible to predict waste line blockages as these can occur at any time during use. Some plastic, "ABS" pipes have shown defects from the manufacturing process and can become weak and break.
Fuel System Natural gall is delivered to the house through underground pipes. On-site fuel storage may consist of oil or propane fuels. Some homes have been converted to natural gas from oil fuel. These homes may have underground fuel tanks still in place which may contaminate the soil. Your inspector is unable to determine the presence of buried fuel tanks.
Water Heater Water heaters are sealed systems which contain a great deal of pressure. The TPR (Temperature & Pressure Relief) valve is a device designed to release excessive pressure from the system. There should be a drain pipe attached to this valve which terminates at a safe location away from body contact. Water heaters sometimes make gurgling noises which are typically the result of built up calcium inside the tank.
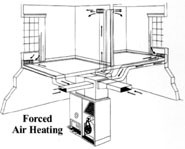
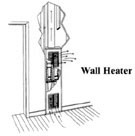
Heating
Description Our description of the heating system includes where the unit is located and the fuel used to generate the heat. Forced air furnaces and water boilers can operate on gas, oil or electricity. Heat pumps utilize electricity to drive the motors and compressors. Furnace size is listed for reference only, if available, and no calculations are performed during this inspection to determine the adequacy or efficiency of the heating system.
Condition Systems are tested using normal homeowner operating controls. If pilots or circuit breakers are off at the time of the inspection, the inspector will not ignite or activate the system. You can contact the utility provider for evaluation of the heating system.
Venting Fuel burning appliances exhaust the products of combustion to the exterior through vent pipes. Vent pipes utilize caps to prevent moisture entry and to stop back drafting. Back drafting means that the products of combustion are escaping into the home instead of venting to the exterior.
Combustion Air When fires burn, they consume oxygen. Fuel that burns completely is harmless and creates only carbon dioxide. Fuel burning appliances must be provided with a constant source of fresh air for the fuels to burn properly. If air is not provided to the fire, incomplete combustion may occur which could produce carbon monoxide. Be sure not to block any air vents around or near your heating systems. Also be advised that maintaining clean air filters is important not only to the air you breathe, but to the operation of the unit as well.
Burners It is impossible to see an entire heat exchanger inside most furnaces, so this inspection does not comment on this component. If there is an uneven or unusual flame pattern or there is rust, charring or deterioration in the burner chamber, we recommend a further investigation of the unit.
Distribution Most heaters utilize some method of moving the furnace generated heat to the rooms which need the heat. Forced air heaters use ducts and registers. Water heating systems use pipes and radiators or convectors. Radiant systems may use pipes or wires if electric. Much of the distribution system will not be visible during this inspection and cannot be judged. For instance, water piping that is buried below or in the concrete floor slab may have leaks that are not detectable without specialized equipment.
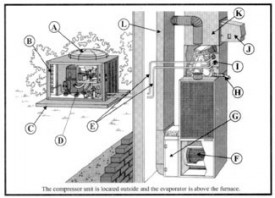
Heat/Cool
Normal Controls Normal operating controls are homeowner operated devices such as a thermostat, wall switch or safety switch. Loose thermostats should be secured and thermostats that are not centrally located or on outside walls should be relocated for better furnace performance.
Air Filters Regular cleaning or changing of air filters is important for proper furnace performance. Dirty filters can cause damage to the heater and waste energy dollars. We do not evaluate the operation of electronic air cleaners but will comment on cleanliness if present.
Heating Notes Our evaluation of the heating system is visual only and does not include dismantling the unit. A service technician should be consulted for an in-depth evaluation, cleaning and adjustment of the furnace for optimum performance and safety. Most local gas companies will perform a safety check and light gas pilots for their customers prior to the heating season. We also do not evaluate humidifiers built onto the heating unit.
Evaporative Cooler Evaporative coolers (commonly called swamp coolers) utilize air flowing across moving water to humidify and cool the house air. Standing water that is left in the unit for extended periods of time can breed bacteria. Evaporative coolers should be drained at the end of each cooling season and cleaned prior to use.
Air Conditioner Air conditioning systems rely on a constant flow of air through the system to properly operate. Restricted air flow from dirty filters or blocked coils can cause icing on the evaporator coil. This may make the air from the unit appear to be colder but is actually harmful for the system. Compressor units located outside should also be kept clear of air restriction. Trim back shrubs and grasses and don' place anything over the tip of the unit that blocks air flow.
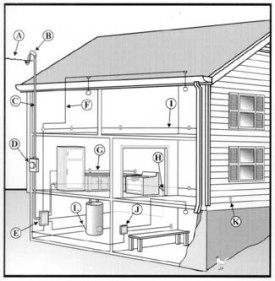
Electrical
Electric Service The electrical service refers to the wires that run from the street or main pole and enter the house either underground or through the rooftop. The number of wires that enter the panel determine the voltage of the service: 2 wires = 120 volt, 3 wires = 240 volt. A home that has only a 120 volt service would be considered out of date by today's standards because larger appliances that operate at 240 volts cannot be utilized. Electrical load and demand calculations are not performed during this inspection.
Main Panel The capacity of the system is determined by the size of the service wires, the rating of the panel and the size o the main fuse or breaker. Some older panels will have fuses while newer systems use breakers. The main disconnect is used to shut the entire electrical system in the house off in case of emergency. If no main shutoff is provided, no more than six breakers are allowed to be installed.
Conductors Conductor is the term used for the wires used for electrical installations. Copper and aluminum are common materials used for electrical wiring. The U.S. Product Consumer Safety Commission issues a booklet on the hazards of aluminum wire installations made in the early 1960's to the mid 1970's. Please obtain this information if aluminum is noted.
Sub-Panel Electrical panels that do not contain the mail service wiring are called sub-panels. Sub-panels are used for a variety of reasons ranging from house size to ease of accessibility. During inspections of homes that are occupied it is possible that a sub-panel might be hidden by pictures or furniture. Please check carefully during your final walk-through of the house after all belongings are removed.
Panel Notes This section of the report notes conditions found inside the electrical panels. Repairs to wiring conditions should be performed by qualified trades people due to the inherent hazards.
Wiring Notes Our inspection of the electrical wiring and fixtures throughout the house will include random testing of outlets and lights. At least one outlet per room, all accessible outlets in the garage and on the exterior, and all outlets within six feet of sinks will be tested for grounding and polarity.
Interior 1
Entry Doors Weather-stripping around the entry door keeps cold air from entering the house. If no weather-stripping is provided we recommend it be installed.
Interior Doors Doors that stick, bind or won't close properly can be adjusted or trimmed to fit. Sometimes however, when doors are out of square and other related conditions are present, it may be an indication of movement in the structure or foundations. If these notes are made, a qualified civil, structural or geo-technical engineer should be consulted.
Exterior Doors Non-safety glass has been used for years in the sliding glass doors of older homes. You should consider upgrading any non-tempered glass doors throughout your home. At times, it is not possible to determine if glass is tempered.
Windows Windows are checked during out inspection. The condition of winter storm windows and doors are not part of this inspection. It is not possible to evaluate the seal on thermo pane windows as conditions change from morning to night and season to season.
Interior Walls In occupied homes, not all portions of all walls will be exposed to view. After the occupants remove all of their belongings, it is wise for you to conduct a final walk-through of the home. look carefully at areas that were not visible during this inspection.
Ceilings Moisture stains on ceilings can come from a variety of sources: plumbing leaks, roof leaks and condensation to name a few. At times it is not possible to determine the cause of a stain. Some older acoustic sprayed ceilings have contained asbestos in the past. Only laboratory testing will accurately reveal asbestos and this testing is not included in the inspection fee.
Floors Our evaluation of the floors in the home is to identify major defects where visible. Stains or odors may be hidden and are not part of this inspection. Once furniture and belongings are removed you will be able to view the condition of floor coverings. Do a careful check on your final walk-through.
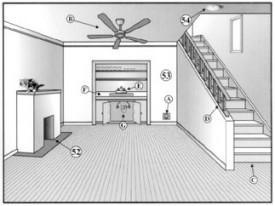
Interior 2
Fireplace Our evaluation of the fireplace does not include a smoke test. Some fireplaces emit smoke into the house during use. If this occurs, a qualified chimney sweep should be contacted for remedy.
Interior Features A - Central vacuum B - Ceiling fan C - Interior stairs D - Stair handrail E - Wet bar faucet F - Wet bar counter G - Plumbing
Smoke Detector Smoke detectors are most effective when located on each floor, in bedrooms and in hallways outside of bedrooms. These units are tested by pushing the test button. Carbon monoxide detectors are new devices that should be considered if fuel burning appliances are installed in the house.
Laundry Washing machines and dryers are not moved or operated during our inspection of the laundry area. Areas behind and under the machines cannot be judged.
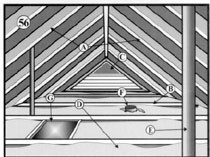
Attic A - Roof framing B - Ceiling framing C - Ventilation D - Insulation E - Plumbing vent pipe F - Recesses ceiling light G - Attic access
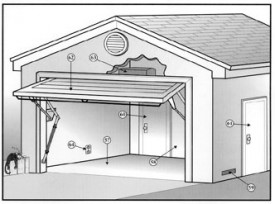
Garage
Floor Garage floors should be constructed of non-flammable materials. Carpeting or other floor coverings should be removed. The floor should also be sloped to drain out the overhead door.
Firewall/Ceiling A wall or ceiling that separates the garage from the house is considered a fire separation. The coverings of these areas should not have large holes. It is typically not possible to determine the rating of these coverings.
Ventilation Ventilation for the garage becomes critical when fuel burning appliances are installed in the garage. These appliances require air for proper combustion.
Door to Living Space The door that enters the house from the garage is considered a fire separation door and should be solid wood, solid core or rated for that location. Pet doors are not allowed.
Exterior Door Sometimes hollow core doors are installed in this location and moisture will delaminate the door skin at the bottom.
Vehicle Door Garage vehicle door types vary from roll-up to tilt-up to sliding. Older door hardware springs are considered unsafe if safety catches arm wires are not provided. For safety, upgrading is recommended for older hardware.
Automatic Opener Garage door opener remote controls are not tested. If a door hits an obstruction during closing is should reverse automatically for safety. Older openers were not equipped with this safety function.
Electrical The garage is a common area for electrical wiring, lights and outlets to be added. All added electrical requires a permit. One of the most common mistakes is using extension cords to power lights or garage door openers.
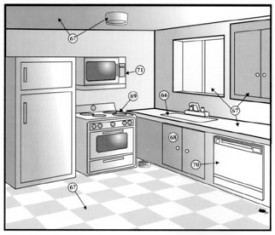
Kitchen
Kitchen Sink Our evaluation of the sink includes turning on the faucet. We check functional flow and look for obvious leaks at the handle and spout. We also run water looking for functional drainage; however, drain lines can become blocked at anytime, and this condition cannot be predicted. Under the sink we check for leaks, rust and corrosion of the sink, drain and supply piping.
General Features General features include: condition of counters, cabinets, flooring, windows, ceiling and light fixtures. Many times dishes and belongings will block view of counters and cabinets. These items are not moved during this inspection and you should check these areas during your final walk-through, and after the occupants have moved out.
Garbage Disposal Garbage disposals can rust and corrode internally. It is difficult to verify the condition of the interior of the unit. If the unit vibrates excessively or makes unusual noises, matter may be lodged inside or blades may be damaged. Sometimes repair is simple, while other times replacement may be required.
Range/Oven/Cook top The elements and burners of ovens, ranges and cook tops are checked for functionality only. Calibration of thermostats is beyond the scope of this inspection.
Dishwasher Our inspection of the dishwasher includes the general condition of the unit, dish racks and door seals. The condition of the pump and motor is not determined since the dishwasher is not disassembled. Racks that are rusted can usually be replaced.
Special Features Special features, if inspected, are tested just as any homeowner would use the device or appliance. No disassembly or special test equipment is used. If there is no trash in a compactor we turn the unit on; however, this does not verify compacting ability. If we operated a microwave we will heat a glass of water for one minute although heating ability varies between units.
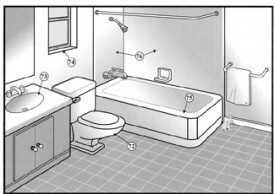
Bathroom
Toilet Toilets that are loose at the base or at the tank connection pose the possibility of leaking. Sometimes the wax seal at the floor must be replaced to prevent leakage on the floor or below the house.
Sink The water shutoff valves below the sink are not tested during this inspection. Many times these valves have not been used for some time and can leak if turned. This is a common occurrence.
Ventilation/Heat Bathrooms that contain a tub or shower need ventilation either through a window or mechanical exhaust vented through the roof or wall.
Bathtub Our evaluation of the bathtub consists of the visible and accessible areas only. Many times the drain and supply piping are not accessible and cannot be judged. Maintaining the caulk and grout in good condition is important to avoid leakage. We do not fill the tub to overflowing to check the overflow drain connection. If a whirlpool is installed we test the equipment using normal operating controls. Sometimes access to the pump and jet piping is not possible and they cannot be inspected.
Shower Shower enclosures should be properly caulked and maintained to avoid leakage. It is often difficult to determine if glass enclosures are tempered safety glass. All non-safety glass is considered a potential hazard and upgrades should be considered.